Common Eye Problems for People with Diabetes

People with diabetes have to protect against many threats to their health, which unfortunately includes their vision and eyesight. As time goes on, diabetes can damage a person’s eyes and cause them to experience poor vision or even blindness. The group of eye problems that affect diabetic individuals is known as diabetic eye disease.
Diabetics with high blood glucose and high blood pressure levels are at a greater risk of developing eye problems if left untreated. Similarly, the risk is also elevated for those that smoke cigarettes or have high blood cholesterol. Thankfully, there are steps that can be taken to prevent eye damage and protect the eyes of someone with diabetes. If caught early on, most diabetes-related vision loss can be prevented with proper care. In this article, we’re going to review some of the common eye issues linked to diabetes. We’ll also review some of the best ways in which diabetic individuals can prevent eye damage.
Some Eye Symptoms Related to Diabetes

Diabetic people usually experience eye issues in both eyes. It’s very important to visit an ophthalmologist right away if you think something is off with your eyesight.
Some signs of concern may include:
- Blurry vision
- Vision loss
- Spotting or floaters
- Light flashes
- Trouble seeing at night
Often times, people may not experience any symptoms at all, even though eyes are being damaged internally. This is why it’s so important for people with diabetes to see their eye doctor on a regular basis. They can catch any signs of trouble early on and prevent this damage from occurring. If these symptoms are not treated, they can lead to more serious issues such as dark spots in your vision, inability to see peripheral things, and blindness.
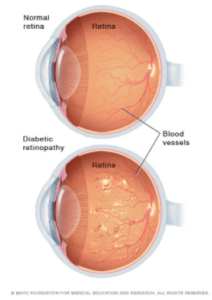
Diabetic Retinopathy
When blood vessels in the back of the eyes get damaged, people with diabetes experience diabetic retinopathy. Although there might not be any symptoms at first, this is a serious condition that can eventually lead to blindness. Anyone with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes is vulnerable to diabetic retinopathy. Although risk can be lowered with good blood sugar management, risk also rises the longer someone has diabetes. As time goes on, high levels of sugar in the blood can cause blood vessels in the retina to get blocked. Unfortunately, this can lead to abnormally developing blood vessels that are prone to leakage.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a condition that puts extra pressure on the eye, resulting in damage to the retina and optic nerve. The optic nerve is very important as it is the central eye nerve for sight. Diabetes has been shown to increase the likelihood that someone will develop glaucoma. Although glaucoma can occur at any age, it is more likely to show up in older adults. This condition is one of the leading causes of blindness for people over the age of 60.
Your eye doctor can help detect glaucoma in the early stages and treat it properly. Ophthalmologists do this by measuring eye pressure during an examination to determine the state of the eye.
Cataracts
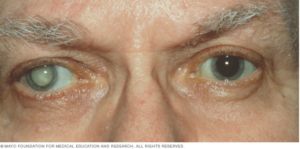
Cataracts occur when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy and leaves people’s vision looking cloudy. Things appear blurry, hazy, or less colorful when cataracts are present. People with diabetes are much more likely to develop cataracts, although maintaining blood sugar levels can help them reduce their risk. These days cataracts can be treated quite well. Surgery is often done to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial one.
Diabetic Macular Edema
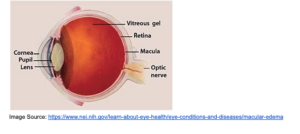
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) occurs when fluid collects in the macula portion of the retina. This can happen because of leakage in blood vessels due to diabetic retinopathy (mentioned above. People with DME often experience blurry vision, floaters, double vision and can suffer from blindness if left untreated. Treatments for DME usually involve laser procedures that aim to stop leakage in the macula.
Conclusion
As you can see, it is very important to protect the eyes if you have diabetes. Make sure to visit your ophthalmologist regularly to catch problems before they start and prevent damage to your vision. Wearing sunglasses also prevents damage that occurs from harmful UVA and UVB rays. Make sure to protect your eyes from the sun to reduce your risk of developing diabetic eye disease. One of the biggest things diabetics can do is control their blood sugar levels properly. Doing so prevents damage to the eye’s blood vessels and reduces the likelihood of developing a variety of eye problems. Staying active can reduce both blood sugar levels, cholesterol, and blood pressure. Find activities that you like to do on a regular basis to increase the likelihood of maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Author Information
Maneeza Hasan is a content marketing professional from Los Angeles, California. She loves to create content that helps people live better lives. To learn more, please visit her website at www.maneeza.com
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]
